|
||||||
|
Solar Energy & Applications |
 |
 |
|
|
|
|
|
Electric generation systems through photovoltaic solar modules have been used globally, mainly due to the ease of their installation, versatility, durability and practically nonexistent maintenance. The generation guarantee with an efficiency greater than 80% in solar modules is over twenty-five years, but its duration exceeds that time.
The modularity of the photovoltaic generator is in its simplicity of increasing the quantity of modules or reducing them, adapting to the intended consumption. You can start with a module and increase as needed. When connecting or disconnecting parts of the system, there is a generator for small equipment to systems with Megawatt power (1 MW = 1 million Watts) to serve cities, for example.
Electricity generation occurs when the panel
is exposed to light (direct or indirect).
b) The second is the "On-Grid": solar system connected to the public electricity grid. This system generates energy during the day and injects the surplus into the grid. At night, without panel generation, will start to consume directly from the grid, inverting and importing electricity. It consists of solar panels and the inverter.
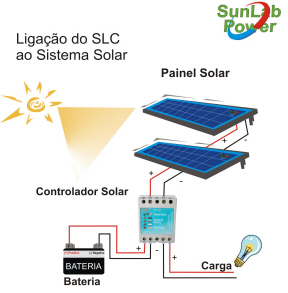
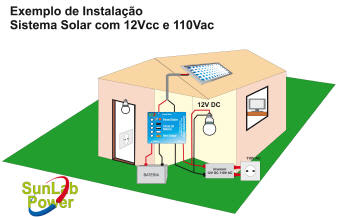
c) The third is what we call "Grid-Tie", or Hybrid: It is a solar system with more than one source of energy generation, sharing the photovoltaic with another, which can be wind, PCH and also connected to the public grid . The system prioritizes one source of energy, charges batteries, as a back-up and can be bidirectional (importer and exporter, such as On-Grid or simply importer, starting to consume from the second source if it is at night and if the batteries are to run out. It consists of solar modules, batteries, charge controller and inverter.
|
|
|
CAN SOLAR ENERGY BE USED TO PROVIDE ELECTRICITY IN PLACES WHERE ELECTRICAL GRID ALREADY EXIST?
Yes. "On-Grid" and "Grid-Tie" systems are connected to the power grid, bidirectional (importer and exporter) in the first case or optionally unidirectional (importer) in the second. The Grid-Tie can be uni or bidirectional.
Photovoltaic generators (PV) can have the most varied applications, not
only in the replacement of the energy source in public grid, but as a
redundant source, back-up, avoiding stoppages of specific systems such
as scientific equipment, security, surveillance, communication, etc ...
|
WHAT TYPES OF APPLIANCES CAN BE POWERED DIRECTLY IN
THE SOLAR SYSTEM?
Practically all, with the correct adequacy. Because the photovoltaic system produces energy in direct current (DC), the first adjustment is the current. For AC installation, is necessary to add the Inverter, wich transforms the current from DC to AC (sinusoidal or alternating) current.
Likewise, the voltage must be
compatible, from the voltage generated by the system to the consumption
voltage. |
|
HOW TO DO TO SUPPLY ELECTRIC HOUSEHOLD APPLIANCES THAT WORK ON ALTERNATE CURRENT?
To power alternating
current devices, as explained above, it is necessary to use an inverter,
which will transform the voltage to 110V or 220V and the direct current
(DC) in the solar system to alternate (AC). |
WHY SOMETIMES THE BATTERY DISCHARGES AND THE SYSTEM STOPS?
The power supply capacity of an Off-Grid solar system is defined in its project. The system must meet the planned consumption (Watts or kW "Kilo-Watts") and its autonomy with some safety margin.
If consumption is at night
and exceeds the generation produced by the panels, the missing will be
supplied by the batteries, and causing, obviously, their discharge.
|
|
WHAT ARE THE MAIN RECOMMENDATIONS FOR IMPLEMENTING A PV SOLAR SYSTEM?
When evaluating the
acquisition of a PV solar system, must be taken that it is an investment
and not an expense. There is a return on your investment if you are
reducing the expenditure on energy from the grid or from another
no-renewable energy generator.
|
WHAT ARE THE MOST USUAL APPLICATIONS OF SOLAR PHOTOVOLTAIC SYSTEM?
Many solar systems and its technologies can be applied to help a lot off human activities. Examples:
. |
|
How to take care of the installation and maintenance of a solar energy system?
It is highly recommended, both in installation and maintenance, to hire
a specialized professional.
The DC connections must
respect the polarities in the equipment that make up the system. Solar
panels must be covered in the installation, avoiding the generation of
energy while in installation. The use of isolated and dry tools is a
necessary precaution, as well as protections (PPE).
Battery systems deserve extra care. Never
short-circuit the poles of the same battery. Always place them in a
ventilated and shaded environment, never exposed to high temperatures. |
|
Typical applications of photovoltaic panels |
|||
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Model House - Solar garden pole |
Residential - pole |
Installation for security |
Industry installation |
|
|
 |
 |
 |
|
Facade, lighting and pumping |
Industry installation |
Installation in buildings |
Solar Station - Power Station |